They activate the same G-protein-coupled receptor luteinizing hormonechoriogonadotropin receptor LHCGR by binding to the large extracellular domain 3. These receptors are often referred to as metabotropic receptors because of the widespread metabolic effects they trigger.
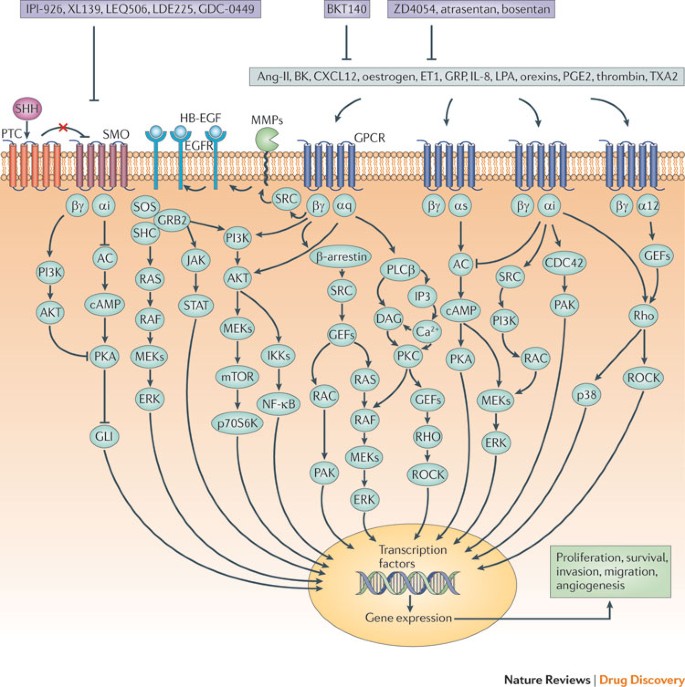
G Protein Coupled Receptors Novel Targets For Drug Discovery In Cancer Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
G-proteins have a vast array of functions and are important for many cellular activities.
G protein hormone receptor system. Gα which carries the binding site for the nucleotide. At least 20 different kinds of Gα molecules are found in mammalian cells. Chung in Hormones and Reproduction of Vertebrates.
Oxytocin a hormone involved in numerous physiologic processes plays a central role in the mechanisms of parturition and lactation. This receptor is associated with an intracellular component called a G protein and binding of the hormone activates the G-protein component Step 2. GPCRs exist as a superfamily of integral membrane protein receptors that contain.
Peptide hormones are secreted and function in an endocrine manner to regulate many physiological functions including growth appetite and energy metabolism cardiac function stress and reproductive physiology. This large receptor family includes light-activated receptors rhodopsins in the eye and literally thousands of odorant receptors in the. These receptors generally function via intracellular second messengers including cyclic AMP cAMP inositol 1 4 5-triphosphate IP 3 and the calcium Ca 2calmodulin system.
G Protein Coupled Receptors GPCRs perceive many extracellular signals and transduce them to heterotrimeric G proteins which further transduce these signals intracellular to appropriate downstream effectors and thereby play an important role in various signaling pathways. It acts through its receptor which belongs to the G-protein-coupled receptor superfamily while Gqphospholipase C PLCinositol 145-triphosphate InsP3 is the main pathway via which it exerts its action in the myometrium. G protein-coupled receptors initiate intracellular signaling cascades and activate downstream effectors when a ligand-bound receptor complex interacts with the G α subunit of the inactive heterotrimeric G-protein complex.
Slow synaptic transmission is mediated by G proteincoupled receptors. G proteincoupled receptors are a single. Many signal via G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs.
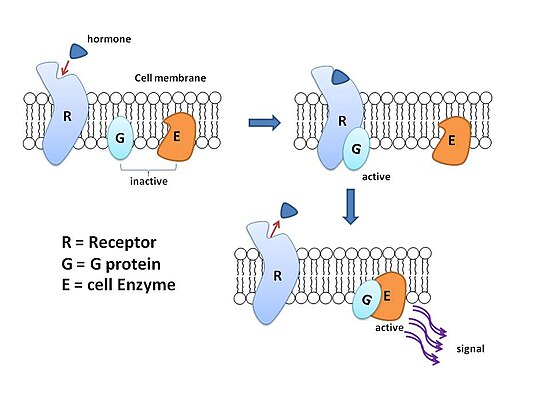
First the alpha subunit of the G- protein loses its GDP and binds a GTP instead. The binding of a signal molecule by the extracellular part of the G-protein linked receptor causes the cytosolic tail of the receptor to interact with and alter the conformation of a G-protein. The activated G protein in turn activates an enzyme called adenylyl cyclase also known as adenylate cyclase Step 3 which converts adenosine triphosphate ATP to cAMP Step 4.
Mammals 2011 32 GnRH-I Receptor Signaling Pathways. Gβ Gγ How They Work. When a hormone or other ligand binds to the.
They are also called G-protein- coupled receptors sensory receptors or ionotropic receptors. Peptide hormones act as ligands for a wide range of G protein-coupled receptors. Once activated G-proteins trigger the production of a variety of second messengers eg.
G proteins relay their signal on the inside surface of the cell membrane. Steroid Hormone Receptors and Related Receptors. Cyclic AMP cAMP inositol triphosphate IP3 diacylglycerol DAG.
G-proteins also trigger intracellular reactions. One of which being cell signaling and cell communication. This beta-subunit helps in adding phosphate groups to the beta-subunits and also to the specific tyrosine residues that are present in the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor.
They are peripheral proteins that are bound to a transmembrane protein or attached to the membrane. Tyrosine kinase enzyme is also present in the beta-subunits. G-protein coupled receptors convert extracellular hormonal signals into intracellular second messengers that produce a physiological response in the target c.
In the inactive state Gα has GDP in its binding site. Therefore this is a key difference between G. This changes the shape of the receptor and it binds to the inactive three-chain G protein inside.
On the other hand receptor tyrosine kinases are enzyme-linked receptors associated with tyrosine and ATP. All G protein coupled receptors GPCRs contain seven membrane-spanning regions with their N-terminal segment on the exoplasmic face and their C-terminal segment on the cytosolic face of the plasma membrane Figure 20-10. G protein coupled receptors and receptor tyrosine kinases are two types of cell surface receptors that mediate cell signalling pathways.
This has two consequences. G-proteins are guanine nucleotide binding proteins. G proteins are associated with hormone receptors on the cytosolic side of the cell membrane.
Neurotransmitters from all three categories interact with G proteincoupled receptors and mediate slow synaptic transmission in the CNS. G protein is a protein that binds either GTP or GDP. The process starts when a receptor binds to its proper hormone or neurotransmitter such as adrenaline shown on the left using PDB entry 3sn6.
The three subunits are. These mediators then help in releasing. Transmembrane receptors of hormones etc.
These receptors are coupled to intracellular GTP-binding proteins G-proteins. G-Protein-Coupled Receptors GPCRs largest family of transmembrane proteins in the human genome with more than 800 unique GPCRs. Here we report four cryo-electron.
G-protein is also activated by some hormones and this in turn activates the phosphodiesterase enzyme. G protein coupled receptors associate with G proteins and GTP. These are called G protein-coupled receptors GPCRs.

How Hormones Use G Protein Signaling Pathways A Video Review Of The Basics Youtube
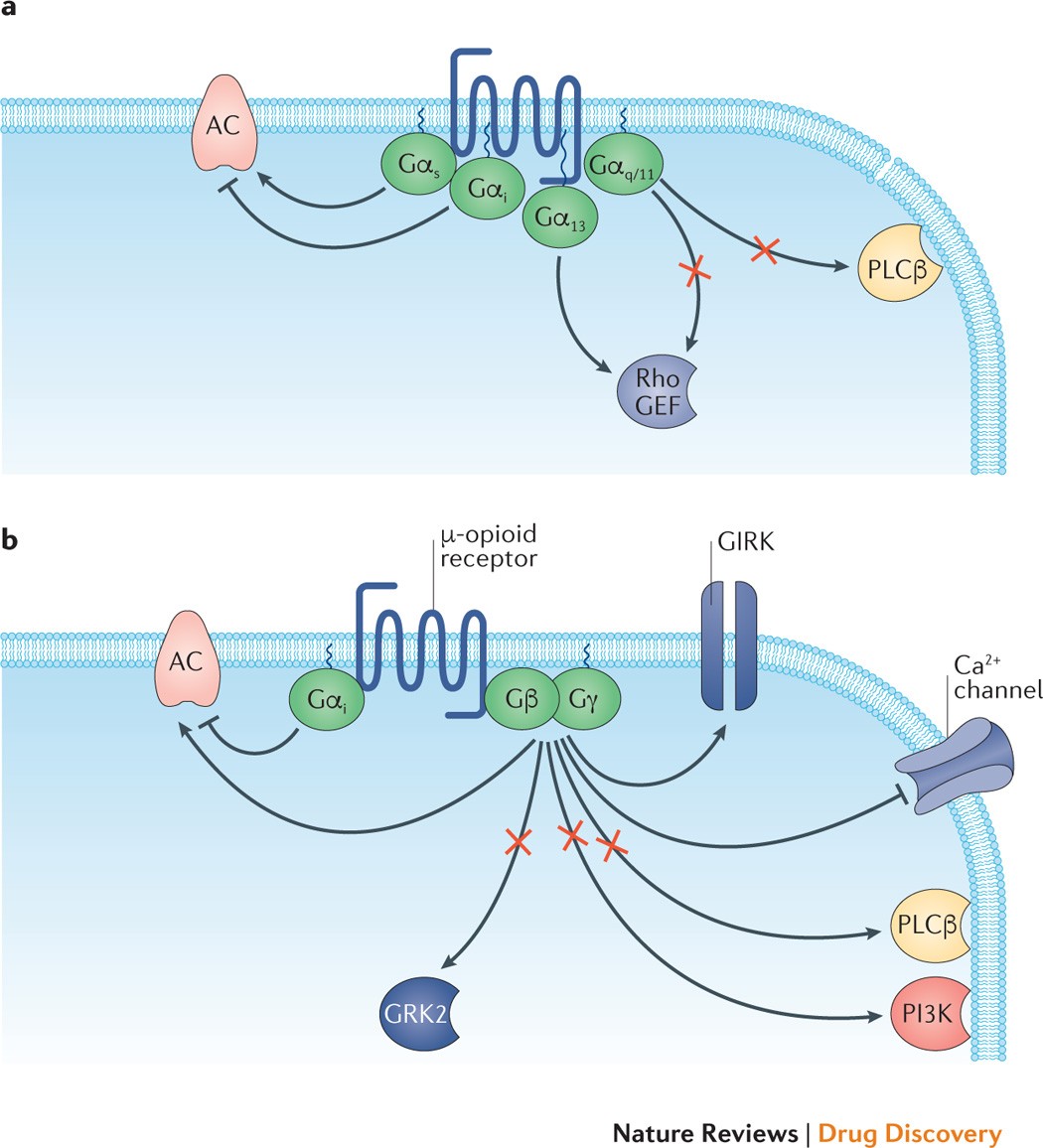
Targeting G Protein Coupled Receptor Signalling By Blocking G Proteins Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
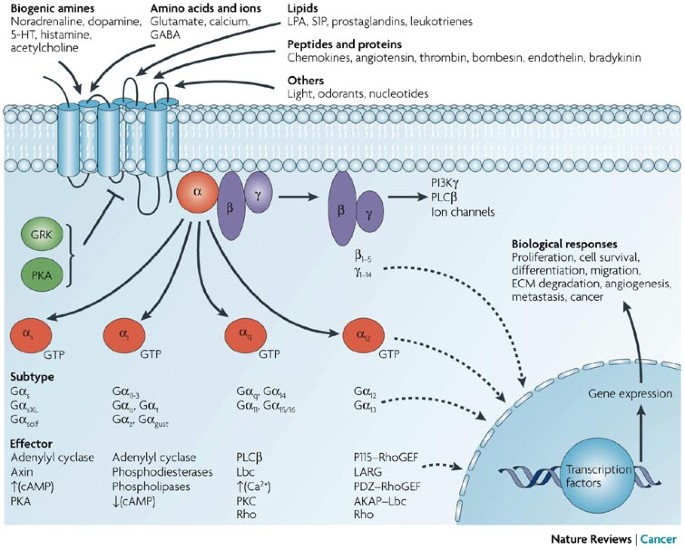
G Protein Coupled Receptors And Cancer Nature Reviews Cancer
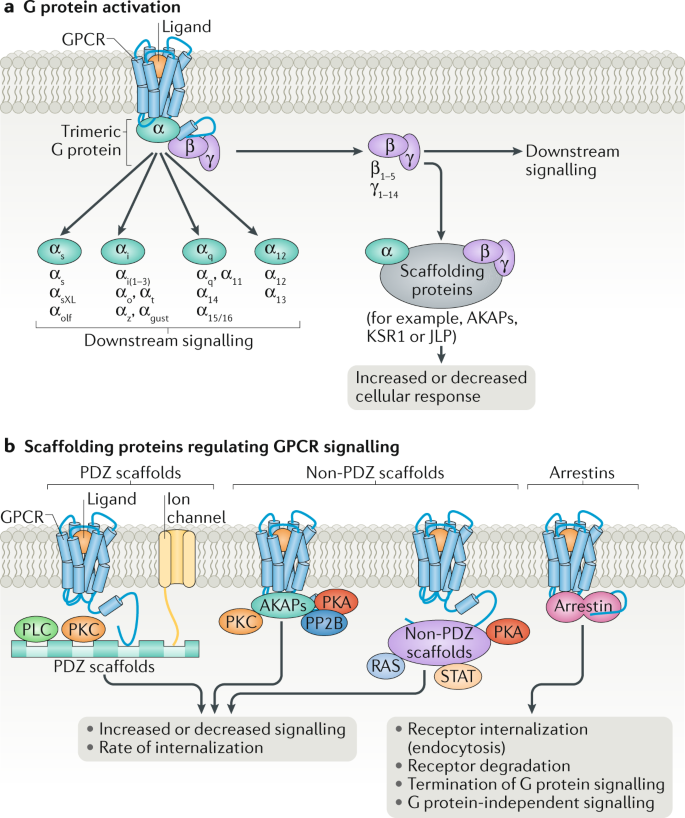
Mechanisms Of Signalling And Biased Agonism In G Protein Coupled Receptors Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology

G Protein Coupled Receptor Gpcr Signaling Via Heterotrimeric G Proteins From Endosomes Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Illuminating The Onco Gpcrome Novel G Protein Coupled Receptor Driven Oncocrine Networks And Targets For Cancer Immunotherapy Journal Of Biological Chemistry
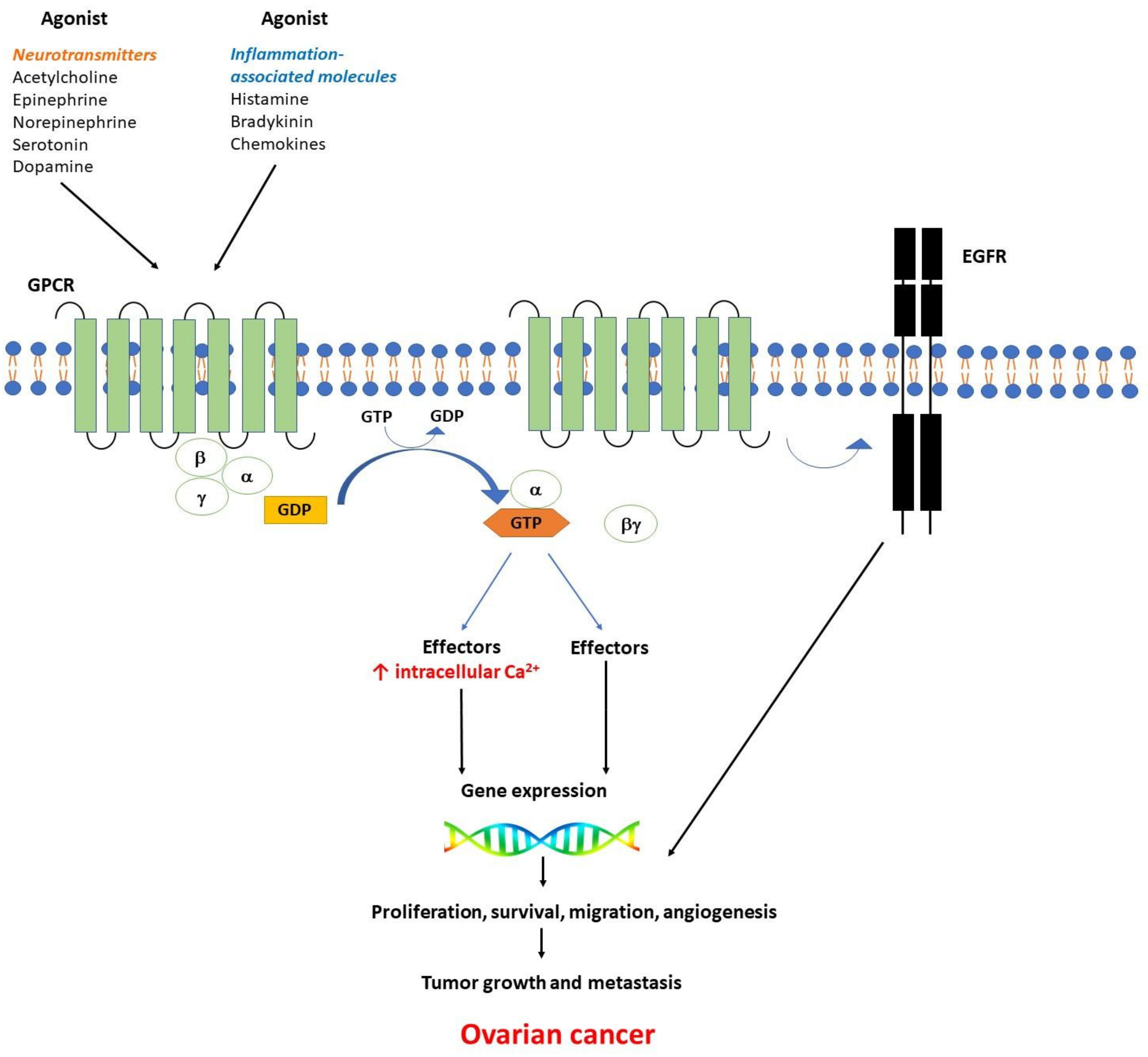
Ijms Free Full Text G Protein Coupled Receptors Gpcrs Mediated Calcium Signaling In Ovarian Cancer Focus On Gpcrs Activated By Neurotransmitters And Inflammation Associated Molecules Html
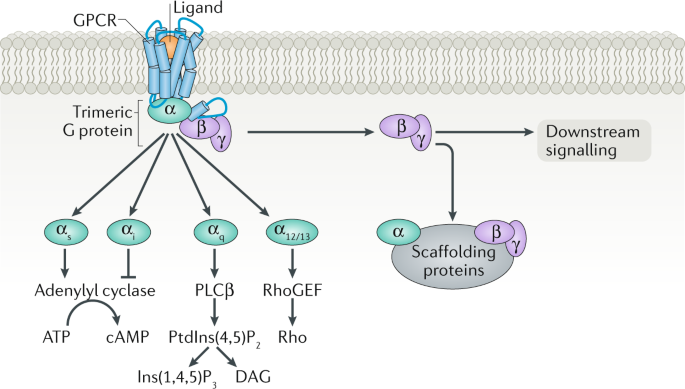
G Protein Coupled Receptor Kinases As Therapeutic Targets In The Heart Nature Reviews Cardiology

Mechanisms Of Adhesion G Protein Coupled Receptor Activation Journal Of Biological Chemistry

The Pathways Connecting G Protein Coupled Receptors To The Nucleus Through Divergent Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase Cascades Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Structural Insights Into Emergent Signaling Modes Of G Protein Coupled Receptors Journal Of Biological Chemistry
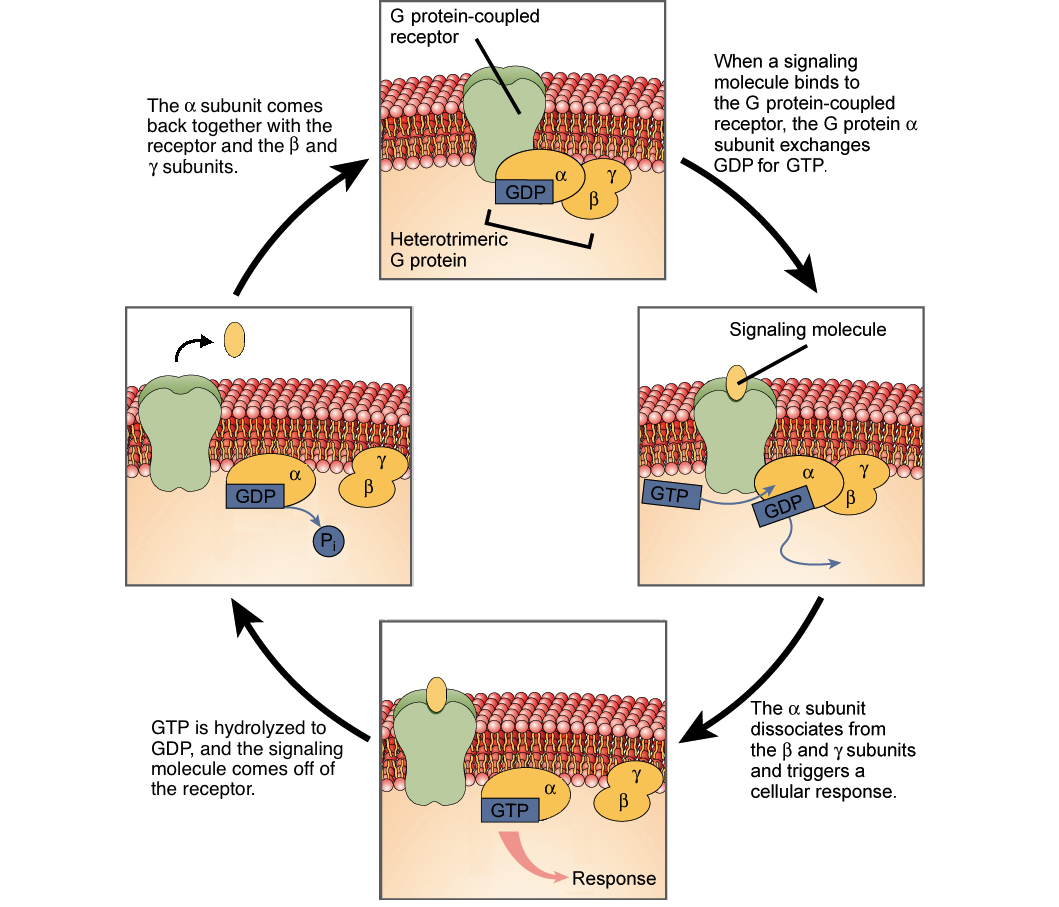
Ligands Receptors Article Khan Academy

G Protein Coupled Receptor Biochemistry Britannica

G Protein Coupled Receptor Wikipedia
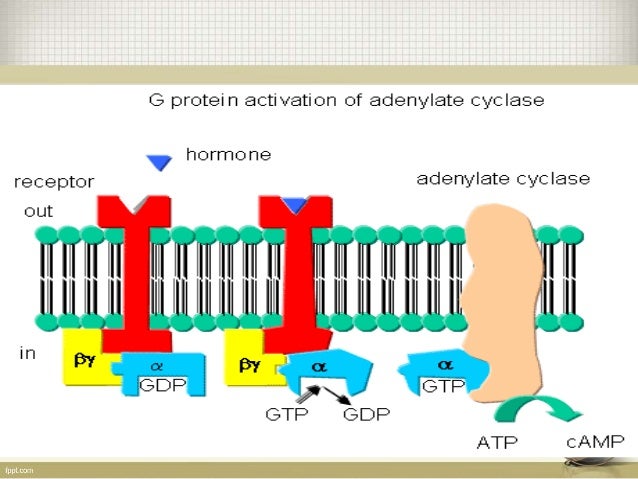
G Protein Coupled Receptors And Their Signaling Mechanism
Biology 107 Lecture Notes Cell Communication

Plasma Membrane Hormone Receptors Biology For Majors Ii
Structural Biochemistry Cell Signaling Pathways G Proteins And G Protein Coupled Receptors Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

G Protein Coupled Receptors And Signaling Networks Emerging Paradigms Sciencedirect
Post a Comment
Post a Comment